
Technics > How to run Apache Httpd and Tomcat on port 80 using mod proxyThis how to assumes you already have installed Apache Httpd and Apache Tomcat running on a Debian/Ubuntu compatible box. Sometimes is it useful to run Apache and Tomcat side by side running on the standard http port (80) in case you need to run other scripts than JSP pages or Servlets. There are several ways to do this. The tomcat project exposes them in the Connector Docs. But in this case we are going to use mod_proxy which is a general propose proxy module. The main idea is to setup a VirtualHost exclusive for tomcat on a given path of our site. Ensure we have mod_proxy enabledYou need to enable 2 modules: proxy and proxy_http using a2enmod root@server# a2enmod proxy
Module proxy installed; run /etc/init.d/apache2 force-reload to enable.
root@server# a2enmod proxy_http
Enabling proxy as a dependency
This module is already enabled!
Module proxy_http installed; run /etc/init.d/apache2 force-reload to enable.
Create your VirtualHostroot@server# cd /etc/apache2/sites-available
root@server# vi mysite.com
This is the content of mysite.com <VirtualHost XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@localhost
ServerName http://www.mysite.com/
DocumentRoot /home/httpd/publics/mysite.com/
ErrorLog /var/log/apache2/mysite.com-error.log
# Possible values include: debug, info, notice, warn, error, crit,
# alert, emerg.
LogLevel warn
CustomLog /var/log/apache2/mysite.com-access.log combined
ServerSignature Off
<Directory /home/httpd/publics/mysite.com/>
Options FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Options -MultiViews
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
Now we need to enable this VirtualHost root@server# a2ensite mysite.com
Site mysite.com installed; run /etc/init.d/apache2 force-reload to enable.
Add your Tomcat VirtualHost
Here lets assume we want to have mysite.com and tomcat.mysite.com where all tomcat request will goroot@server# cd /etc/apache2/sites-available
root@server# vi tomcat.mysite.com
This is the content of tomcat.mysite.com <VirtualHost XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@localhost
ServerName tomcat.mysite.com
DocumentRoot /home/httpd/publics/tomcat.mysite.com/
ErrorLog /var/log/apache2/tomcat.mysite.com-error.log
# Possible values include: debug, info, notice, warn, error, crit,
# alert, emerg.
LogLevel warn
CustomLog /var/log/apache2/tomcat.mysite.com-access.log combined
ServerSignature Off
# lets indicate the proxy what path do we want
# to forward to tomcat
ProxyPass / http://localhost:8080/
<Directory /home/httpd/publics/tomcat.mysite.com/>
Options FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Options -MultiViews
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
Now we need to enable this VirtualHost too root@server# a2ensite tomcat.mysite.com
Site tomcat.mysite.com installed; run /etc/init.d/apache2 force-reload to enable.
Restart Apache
The trickThe main trick of this configuration resides on the line - ProxyPass / http://localhost:8080/
Where we tell the proxy what path should be forwarded to Tomcat. In the same way we could modify this to our needs. Lets say we would like to have our path on /tomcat/ all we should do is:
The advanced way
We may want to run both VirtualHost in the same configuration and only forward to tomcat requests starting on a given path
<VirtualHost XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@localhost
ServerName mysite.com
DocumentRoot /home/httpd/publics/mysite.com/
ErrorLog /var/log/apache2/mysite.com-error.log
# Possible values include: debug, info, notice, warn, error, crit,
# alert, emerg.
LogLevel warn
CustomLog /var/log/apache2/mysite.com-access.log combined
ServerSignature Off
# lets indicate the proxy what path do we want
# to forward to tomcat
ProxyPass /java/ http://localhost:8080/
<Directory /home/httpd/publics/mysite.com/>
Options FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Options -MultiViews
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
With the above scheme all requests will be served by apache unless they start with /java/ Will be served by the PHP engine. But however: Will be forwarded to Tomcat |
|
Apache Tomcat and the World Wide Web
Usually when running an application server, such as Apache Tomcat, you bind a connector directly on port 80. This way users visiting your web application will be able to navigate through your server just by calling your domain instead of calling your domain and special port (http://yourdomain.com:8080). If there is no option to bind a Tomcat connector on port 80 (some systems ban this functionality for security purposes), there are other ways to achieve this behavior such as setting a redirect on port 80 to port 8080 (Tomcat’s default, or any other) using IPTables or any other port redirection tool. Both options are really simple procedures, but are a great issue if you need to run a simple HTTP server on your machine too.
Apache and Tomcat on the same server with modjk (Note: mod-jk2 is deprecated, use mod-jk) If you are having apache and tomcat on the same server, you can use the old way of mod-jk. Note however mod-jk2 is now deprecated and you have to use mod-jk (1). In my last post (Virtual Host in Tomcat) we discussed about how setup the virtual host in Tomcat. Its cost effective technique because only one public IP is. There are many ways to compare Tomcat vs. The Apache HTTP Server, but the fundamental difference is that Tomcat provides dynamic content by employing Java-based logic, while the Apache web server's primary purpose is to simply serve up static content such as HTML, images, audio and text. Go back to the Apache Tomcat home page, and download the Windows Installer (either 32- or 64-bit as needed): Once the download is complete, click on Next. Then you’ll need to agree to the License Agreement. Apache Tomcat offers a highly customizable installation process. In fact, you’re able to omit the various add-ons that can be included.
Apache Tomcat Error 404
Apache HTTP and mod_proxy
To solve this problem we can run Apache HTTPD as a front-end proxy for Apache Tomcat and redirect traffic to the application server based on a set of rules. In this tutorial we will use mod_proxy, although there are many other options available.
This tutorial assumes that Apache Tomcat is already installed and configured with the default connector settings (port 8080) and Apache HTTP is installed too with the default listener settings (port 80).
For this tutorial we are going to assume that there are 2 different domains (tomcatserver.com and httpserver.com) pointing to the same IP address. The user expects to reach the application server when navigating to one domain and the web server when navigating to the other.
First step is make sure that the file httpd.conf has mod_proxy enabled (which is by default), so in case it isn’t, uncomment the following line.
LoadModule proxy_module modules/mod_proxy.so
Taking into account that there are 2 domains, we need to use the NameVirtualHost directive and define two virtual hosts based on the different domains.
NameVirtualHost *:80

Next we define the virtual host that will redirect traffic to tomcat. In case tomcat has some virtual hosts defined too, we’ll add a ServerAlias for each domain that needs to reach tomcat
| ServerAdmin root@localhost ServerName httpserver.com ServerAlias httpserver1.com </VirtualHost> |
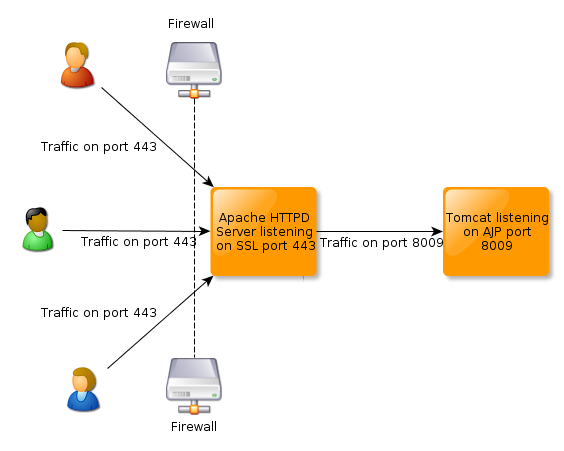
Proxy Rules
Apache Tomcat Httpd.conf

Apache Httpd Tomcat Load Balancing
In this example we’ve assumed there are two different domains (or more) and that each domain will point to a different type of server. mod_proxy allows us to define more advanced rules, to proxy content based on other rules such as the context path.



